Hyperthyroidism and Iodine Deficiency
Iodine is vital for the development of our brain cells and for the regulation and production of the thyroid hormones. Lack of iodine can lead to a disorder of the thyroid gland called as hypothyroidism. In this disorder, production of the thyroid hormones, such as thyroxine, is suppressed. While treating hypothyroidism, there is always a risk of developing hyperthyroidism due to overzealous treatment. In hyperthyroidism, there is excessive secretion of thyroxine. Deficiency of iodine can be life-threatening for the health and it might be an indicator of some underlying health issue.
 Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
The thyroid gland is small in size yet it is the master gland of our body. It is located in the front of our neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It produces the thyroid hormones, such as triiodothyronine and thyroxine. Hyperthyroidism is a disorder of the thyroid gland in which the thyroid become overactive and produces excessive amounts of thyroxine. Symptoms like drastic increase in the basal metabolic rate, resulting in rapid weight loss, sweating, an irregular or accelerated heartbeat, irritability and nervousness etc. can occur in this condition. Besides the deficiency of iodine, other culprits behind the hyperthyroidism can be Plummer’s disease, Graves’ disease, thyroiditis and toxic adenoma.
Deficiency of Iodine
Our body needs iodine for the production of thyroid hormones, such as triiodothyronine and thyroxine. These hormones play a role in the development of cognitive system of infants and in the regulation of our metabolic functions.
The lack of iodine usually stems from insufficient intake of dietary iodine and it can cause grave complications, for example irreversible damage to the cognition of newborns and metabolic derangement, like hyperthyroidism. According to the WHO, iodine deficiency is the major cause of avoidable mental retardation. Studies done on the American population shows that their iodine intake is above average, but certain exceptions are there and in some cases deficiencies might occur, for example in post- menopausal and pregnant women.
Role of Iodine
Radioactive iodine is used as a cure for a hypoactive thyroid gland or hypothyroidism. It is taken orally to shrivel the thyroid gland up and it can take 3 to 6 months for the symptoms to settle down. Nonetheless, this will also suppress the activity of your thyroid and you might be required to take measure to substitute for the consumed levels of the thyroxine hormone.
 This balance of the thyroid hormones and iodine levels is extremely sensitive and the overzealous treatment for the hypothyroidism can produce the reverse disease, i.e. hyperthyroidism.
This balance of the thyroid hormones and iodine levels is extremely sensitive and the overzealous treatment for the hypothyroidism can produce the reverse disease, i.e. hyperthyroidism.
Preventive measures
For the treatment of hypothyroidism, radioactive iodine plays an essential role but at the same time a suitable supply of dietary iodine must be ensured to keep the thyroid gland healthy. Standard values for the intake of iodine in the diet is 150 micrograms per day in the case of adult women and men, while in lactating and pregnant women the intake should be increased to 290 and 220 micrograms, respectively.
Natural sources of iodine include eggs, seafood, dairy and grains etc. Sea plants, for example seaweed and kelp are rich in iodine. Using an iodized salt can also ensure an adequate intake of dietary iodine.

 Subscribe Now
Subscribe Now

 Recommended Daily Amounts for Iodine Intake
Recommended Daily Amounts for Iodine Intake Our body is neither capable of manufacturing or storing iodine. Therefore, it is important to keep a maintained supply of iodine in the diet. Food items like cheese, eggs, seafood and yogurt are rich in iodine. Other examples included vegetables and fruits grown in the soil rich in iodine. On the contrary, areas which have a low content of iodine in the soil, produce food items low in the iodine content. Residents of such areas are more prone to develop iodine deficiency. On the other hand, there are certain foods abundant in goitrogens, such as cabbage, cauliflower and broccoli etc. The
Our body is neither capable of manufacturing or storing iodine. Therefore, it is important to keep a maintained supply of iodine in the diet. Food items like cheese, eggs, seafood and yogurt are rich in iodine. Other examples included vegetables and fruits grown in the soil rich in iodine. On the contrary, areas which have a low content of iodine in the soil, produce food items low in the iodine content. Residents of such areas are more prone to develop iodine deficiency. On the other hand, there are certain foods abundant in goitrogens, such as cabbage, cauliflower and broccoli etc. The 
 Hair and Thyroid Function
Hair and Thyroid Function If you are suffering from coarse hair or hair loss, the underlying cause might be a thyroid disorder. You might consult a doctor for this, who will conduct tests for determining your thyroid function and iodine status, in order to rule out iodine deficiency as a cause. If a diagnosis of thyroid disease due to lack of iodine is made, you might be given iodine prescriptions, as a cure. But
If you are suffering from coarse hair or hair loss, the underlying cause might be a thyroid disorder. You might consult a doctor for this, who will conduct tests for determining your thyroid function and iodine status, in order to rule out iodine deficiency as a cause. If a diagnosis of thyroid disease due to lack of iodine is made, you might be given iodine prescriptions, as a cure. But 
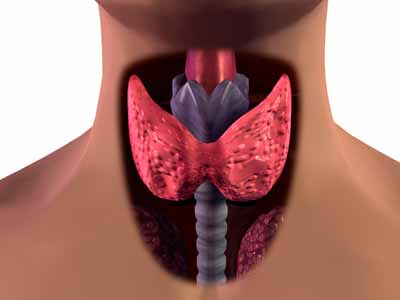 Anatomy and Location
Anatomy and Location Goiter: It is a swelling which forms in the region of our neck. A goiter associated with hyper active thyroid is called toxic. On the other hand, an endemic or simple goiter is a goiter caused by the deficiency of iodine and it is non-toxic in nature.
Goiter: It is a swelling which forms in the region of our neck. A goiter associated with hyper active thyroid is called toxic. On the other hand, an endemic or simple goiter is a goiter caused by the deficiency of iodine and it is non-toxic in nature.

 Exact
Exact 
 Causes
Causes Relation of Goiter with the Dietary Factor
Relation of Goiter with the Dietary Factor
 Thyroid and Iodine
Thyroid and Iodine Seaweed is also a great source of selenium. Studies have shown that the selenium is essential for the conversion of thyroxine hormone into threonine hormone. In the absence of selenium, this conversion would not take place and hence no thyroid hormones will be produced. The recommended daily allowance, or the RDA, of selenium and iodine is 55 mcg and 150 mcg per day, respectively.
Seaweed is also a great source of selenium. Studies have shown that the selenium is essential for the conversion of thyroxine hormone into threonine hormone. In the absence of selenium, this conversion would not take place and hence no thyroid hormones will be produced. The recommended daily allowance, or the RDA, of selenium and iodine is 55 mcg and 150 mcg per day, respectively.
 Causative Agents for Goiter
Causative Agents for Goiter




 Cruciferous veggies are rich in sulfur containing compounds such as glucosinolates. Byproducts of these compounds, known as isothiocyanates, are produced when glucosinolates are broken down. According to an elaborate research these byproducts, isothiocyanates, can block the uptake and absorption of iodine by our thyroid gland, thus leading to the formation of a goiter. Goiter is essentially caused by the deficiency of iodine and consumption of cruciferous vegetables produces a relative lack of iodine by hindering effects of iodine on the functions of thyroid. Some examples of such vegetables are Brussels sprout, turnips, broccoli, cabbage, bok choy, collards, cauliflower, turnips, kohlrabi, rutabaga,
Cruciferous veggies are rich in sulfur containing compounds such as glucosinolates. Byproducts of these compounds, known as isothiocyanates, are produced when glucosinolates are broken down. According to an elaborate research these byproducts, isothiocyanates, can block the uptake and absorption of iodine by our thyroid gland, thus leading to the formation of a goiter. Goiter is essentially caused by the deficiency of iodine and consumption of cruciferous vegetables produces a relative lack of iodine by hindering effects of iodine on the functions of thyroid. Some examples of such vegetables are Brussels sprout, turnips, broccoli, cabbage, bok choy, collards, cauliflower, turnips, kohlrabi, rutabaga,  Soy Products
Soy Products