Top Goiter Treatments
A goiter can be toxic or non-toxic. A goiter that is non-toxic is simply an enlargement of the thyroid gland, which is not linked to malignancy or excessive production of the thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland can enlarge excessively and can be seen as a huge swelling in front of the neck. Normally, this gland is butterfly in shape, but with the enlargement, its shape can distort. There are a number of causes for goiter. In the past, the lack of iodine used to be the major culprit for this disorder but now it has become a rare occurrence because of the incorporation of iodized salt in our diet. Nowadays, rise in TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) level contribute to the formation of goiter mostly. This rise in TSH levels occurs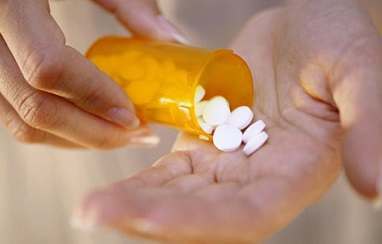 insidiously and can be precipitated by defective synthesis of thyroid hormones. TSH is synthesized by the pituitary gland and it can enlarge our thyroid gland.
insidiously and can be precipitated by defective synthesis of thyroid hormones. TSH is synthesized by the pituitary gland and it can enlarge our thyroid gland.
Thyroid Drugs
Thyroid drugs can be used for the treatment of moderate or small sized goiter. These thyroid drugs mimic like thyroid hormones, thus sending signals to the pituitary to produce less TSH. This, in turn, leads to the stabilization of the size of the thyroid gland. This method will probably not shrink goiter but it will prevent it from enlarging any further.
Thyroid Surgery
Following are some indications for thyroid surgery:
- If a person does not respond to the thyroid drugs, then the best, next step is to opt for the surgery.
- Another major indication for the surgery is pressure symptoms, for example the compression of esophagus and trachea, caused by a grossly enlarged goiter. Such patients complain of symptoms, such as cough, change in the quality of voice, choking episodes while sleeping; because on lying down the heavy goiter occludes the trachea thus producing the difficulty in breathing.
- The thyroid gland has two lobes. Either both or a single lobe can be enlarged due to goiter. If only one lobe is enlarged, this can lead to the displacement of trachea, which normally runs straight from our mouth to our lungs.
- In some case, the enlarged goiter can even squeeze our blood vessels which are running through the neck. This is an important indication for the surgical removal.
 Malignancy is always an indication for the removal of thyroid gland. So, if there is any suspicion of malignancy, go for the surgery.
Malignancy is always an indication for the removal of thyroid gland. So, if there is any suspicion of malignancy, go for the surgery.- In a multi-nodular goiter, the chances of malignancy are slightly less than five percent. Presence of a dominant nodule in a multi-nodular goiter, raises the suspicion of malignant goiter. Same principle applies for a scan showing a cold nodule in the thyroid gland.
- Lastly, a goiter can be removed for the cosmetic reasons. Sometimes it can enlarge enough to be noticed as a swelling, mostly in the front and sides, of the neck. This mass, or swelling, can be seen with the naked eye, even before the pressure symptoms occur. This can be a source of unease for some people. They can try, either thyroid medications or the surgical removal of thyroid, for getting rid of their goiter.

 Subscribe Now
Subscribe Now