
Everything You Should Know About Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a state in which our thyroid gland becomes hyperactive and secretes increased amounts of the thyroid hormones. Basically, the thyroid is a gland which is butterfly in shape and is located a little below our Adam’s apple, in front of our neck. The hormones released by this gland regulate our breathing, body temperature, heart rate, and metabolism, weight, nervous system and various other functions of our body. When our thyroid gland is hyperactive, the increased hormone production speeds up our bodily functions, thus causing the following symptoms:
- Tremors of hand

- Excessive sweating
- Rapid heart rate
- Anxiety
- Nervousness
- Sleep problems
- Loss of weight
- Diarrhea
- Mood swings
- Irregular heart beat or palpitations
- Dryness of the skin
- Muscle weakness or fatigue
- Trouble with sleep
- Menstrual irregularities, such as no periods or light flow during periods.
- Sometimes, a swelling might be present in front of the neck showing an underlying goiter.
Reasons Of Hyperthyroidism
Triiodothyronine and thyroxine, are also known as T3 and T4, respectively. These are thyroid hormones produced by the thyroid gland. Autoimmune disorder i.e. the Graves’ disease is the most usual cause of a hyperactive thyroid. In this condition, the body produces an antibody called TSI (thyroid stimulating immunoglobulin). TSI stimulates the thyroid to produces more thyroid hormones. It occurs mostly in middle- aged females and runs in kith and kin.
Either a toxic multi-nodular or nodular goiter can present as hyperthyroidism. Nodular goiters feel lumpy on palpitation during thyroid examination. Hyperthyroidism can also result from the thyroiditis. In addition to that, it can also occur in people who are taking medicines containing iodine (for example amiodarone) or those who consume lots of iodine (either in the form of supplement or iodine-rich foods). Lastly, some females can suffer from hyperthyroidism either during the pregnancy or during the first year following the birth of the baby.
Establishing The Diagnosis
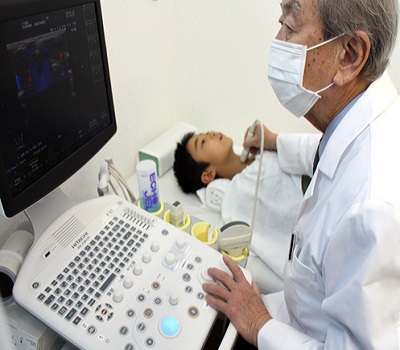 Hyperthyroidism can be diagnosed on the basis of history of symptoms, physical examination of the thyroid gland and blood test for checking the levels of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) and the thyroid hormones i.e. T4 and T3. In special cases, your physician might order a radioactive iodine uptake test or an ultrasound of the thyroid to examine it more closely for inflammation, nodules and hyperactivity.
Hyperthyroidism can be diagnosed on the basis of history of symptoms, physical examination of the thyroid gland and blood test for checking the levels of TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone) and the thyroid hormones i.e. T4 and T3. In special cases, your physician might order a radioactive iodine uptake test or an ultrasound of the thyroid to examine it more closely for inflammation, nodules and hyperactivity.
Treatment Options For Hyperthyroidism
A hyperactive thyroid can be controlled with anti-thyroid drugs. These drugs can block the output of hormones from the thyroid gland. Examples of such drugs are propylthiouracil, methimazole etc. Nowadays, only pregnant women use propylthiouracil, during their first trimester. Another available option is therapy with the radioactive iodine. The radioactive iodine is taken up by the thyroid cells and thus it destroys them. In some instances, women were found to have side effects to the radioactive iodine or lack of response to such therapies. Such women must be offered thyroid surgery. In thyroid surgery, a part or whole of the thyroid gland is removed. The selection of treatment depends upon factors like age, symptoms, severity of the disease, underlying cause, presence of pregnancy, other co-morbidities and possible side effects of the medicines.
TOP 5
THYROIDProducts |
|||||
| Thyraid | ThyroMend | Thyrene | SupraHealth | Blue Spring | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Price (1 bottle) Price (6 bottles)best value |
$49.95 $139.80 |
$38.95 $233.70 |
$39.99 $159.96 |
$59.97 $323.84 |
$35.99 $194.35 |
| Overall Rating | 99.50% | 85.70% | 76.60% | 68% | 60.20% |
| Performance* |





|





|





|





|





|
| Speed of Results* | Extremely Fast | Good | Average | Average | Slow |
| Quality of Ingredients | Premium | Good | Good | Average | Average |
| Customer Satisfaction Evaluation | 99.20% | 84% | 74% | 68% | 60% |
| Safety Evaluation | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use | Safe for Use |
| Customer Service Rating |





|





|





|





|





|
| Reorder Rate | Highest | Good | Good | Average | Average |
| Return Policy | Risk Free | Risk Free | Handling & Restocking Fee | Risk Free | Risk Free |
| Success Rate | 99.20% | 85% | 69.20% | 67.50% | 60% |

 Subscribe Now
Subscribe Now











